Retinal Detachment Surgery
Retinal Detachment Surgery
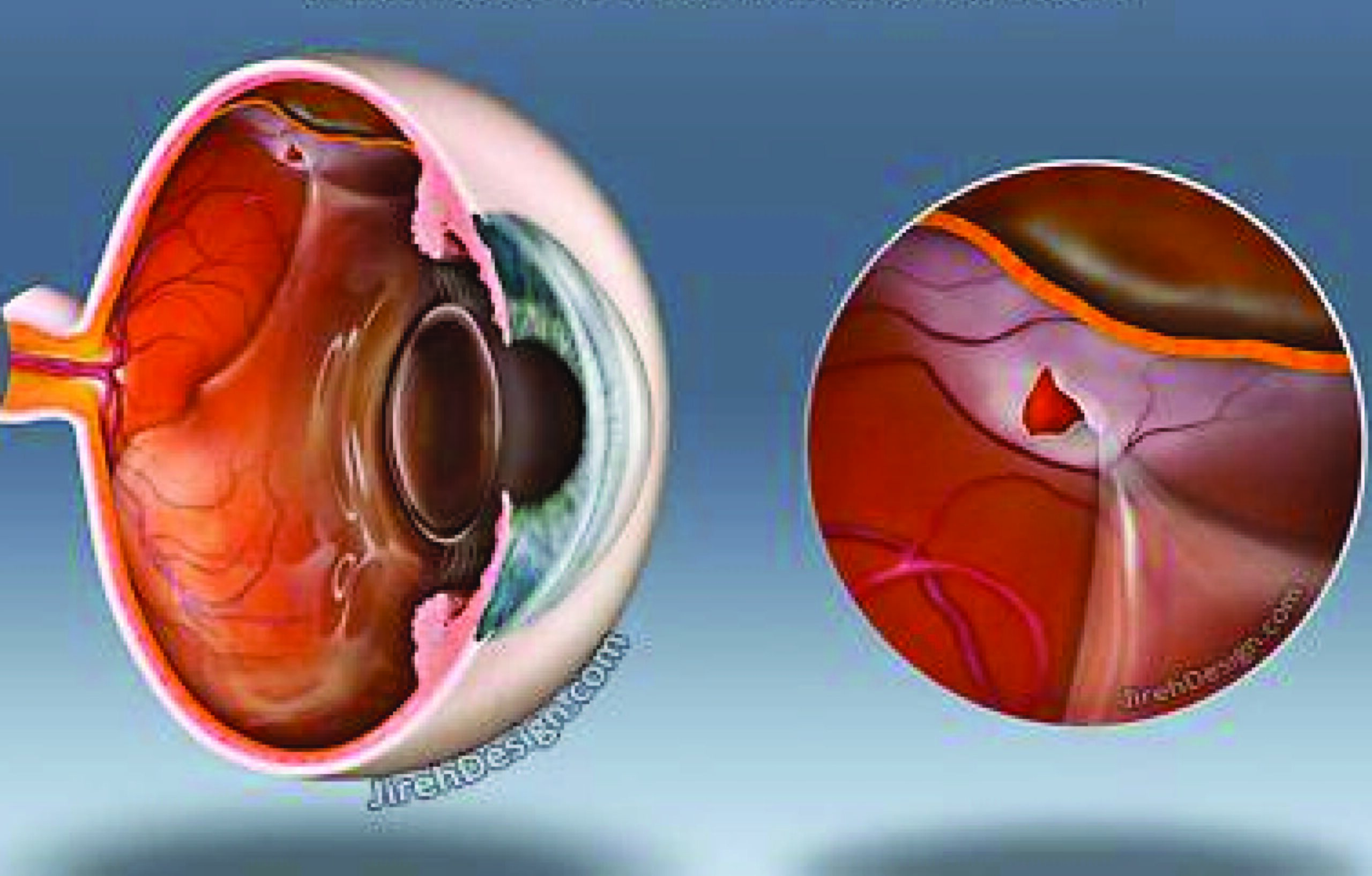
Retinal detachment surgery is a procedure used to reattach the retina to the back of the eye when it has become detached. A retinal detachment occurs when the retina, a thin layer of tissue at the back of the eye responsible for sending visual signals to the brain, pulls away from its normal position.
There are several surgical techniques used to treat retinal detachment, and the specific approach chosen depends on the type and location of the detachment. Here are some common methods:
Scleral Buckle Surgery
In this procedure, a silicone band (scleral buckle) is placed around the outer surface of the eye to gently push the sclera (the white part of the eye) closer to the detached retina. This helps to reattach the retina.
The surgeon may also drain any fluid or blood from under the detached retina.
Vitrectomy
This procedure involves removing the vitreous gel from the center of the eye. The vitreous is the gel-like substance that fills the eye.
Once the vitreous is removed, the surgeon can access and repair the detached retina using small instruments, including lasers or cryotherapy (freezing).
In some cases, a gas or silicone oil bubble is injected into the eye to help reattach the retina. Over time, the bubble is absorbed, and the eye’s natural fluids take its place.
Pneumatic Retinopexy
This procedure is suitable for certain types of retinal detachment. A gas bubble is injected into the vitreous cavity, which helps push the detached retina back into place.
The patient must maintain a specific head position for several days to keep the gas bubble in the correct position.
Combination Surgery
Sometimes, a combination of techniques may be used to reattach the retina effectively. For example, a scleral buckle may be combined with a vitrectomy.
Corneal Removal
The damaged or diseased cornea is carefully removed from your eye using specialized surgical instruments.
Laser or Cryotherapy
In some cases, laser or cryotherapy may be used to seal small retinal tears or holes, preventing further detachment.
Postoperative Care
After the surgery, you’ll receive specific instructions for postoperative care. This may include using prescribed eye drops, avoiding certain activities, and attending follow-up appointments.
It’s important to note that the specific surgical approach chosen will depend on the type, location, and severity of the retinal detachment, as well as the surgeon’s judgment.
Recovery and outcomes can vary based on individual circumstances. Some patients may experience improved vision relatively quickly, while others may take longer to see significant improvements. As with any surgical procedure, there are risks associated with retinal detachment surgery, and your surgeon will discuss these with you before the procedure.
Always consult with a qualified healthcare professional or retinal specialist for the most current information regarding retinal detachment surgery.

